What is the name of the flat plains on the moon?
relatively smooth, flat plains on the Moon. The Caloris Basin on Mercury covers a large region of the planet, but few smaller craters have formed on top of it. From this we conclude that. the Caloris Basin formed toward the end of the solar system's period of heavy bombardment.
Where is the arrow on the moon?
The first arrow points to the large uniformly dark area on the Moon's surface. The second arrow points to the huge dark ring with white center located in the bright area of the Moon, at the bottom of the visible side. The third arrow points to the large uniformly bright area on the Moon's surface.
Why is the color yellow arbitrary?
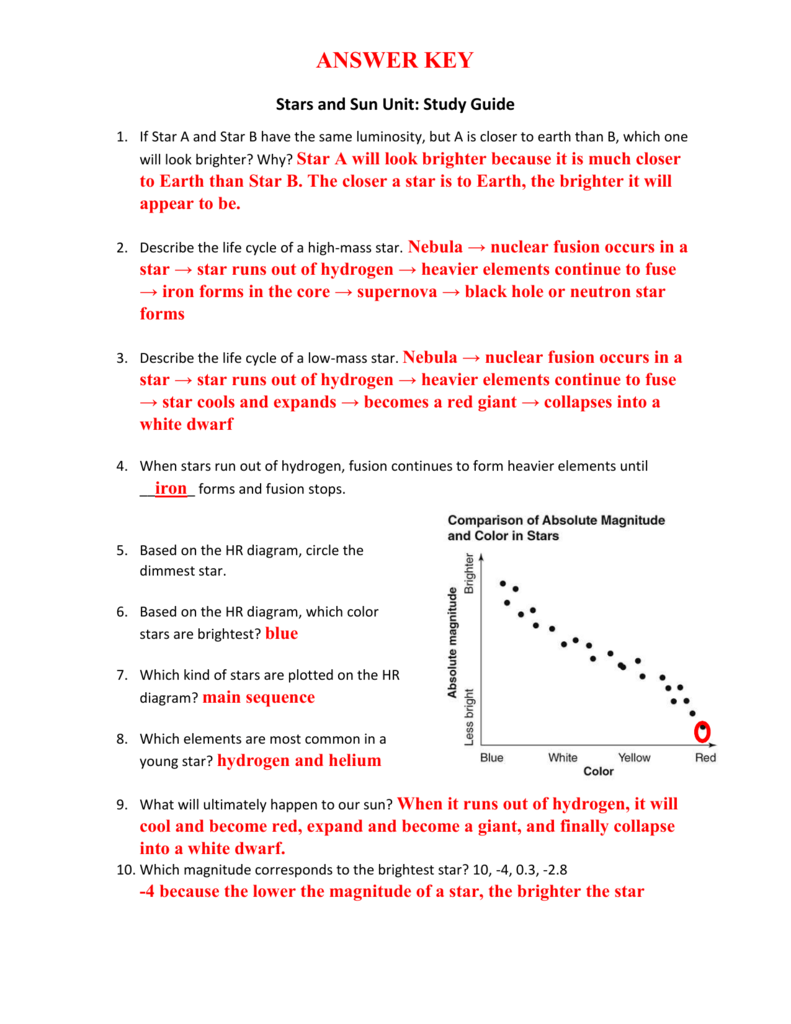
The yellow color is arbitrary because this image was created with radar data rather than visible light. The figure shows the relief map of Earth. There are several yellow lines on this map. One of them goes along the western edge of North America, from North to the South. Then it divides into two lines, one follows the western edge ...
Where is the label 4?
Label two is placed here. Label four is placed at the eastern edge of North America.
Where are convection cells located?
The bottom of the layer corresponds to the upper mantle. Convection cells are located in the middle of the layer. They are indicated by the cycled arrows. Label three is placed inside one of the convection cells below North America. There are also brown arrows, which show the movement of the plates.
What are shield volcanoes made of?
Shallow-sloped shield volcanoes are made from lava that. has a medium viscosity. The photo shows a fragment of the planet's surface. It has a beige color, and there are a few craters, cliffs, and patterns, which look like branches, on the surface. This photo was taken from orbit around some planet.
Popular Posts:
- 1. blackboard udf
- 2. blackboard api web services
- 3. how to upload a file to an assignment on blackboard youtube dmacc
- 4. pa cyber blackboard collaborate login
- 5. what are submitted but not graded items in blackboard
- 6. my blackboard is missing a class
- 7. liberty blackboard university
- 8. lamar blackboard
- 9. how to attach link blackboard
- 10. uic add learning module blackboard